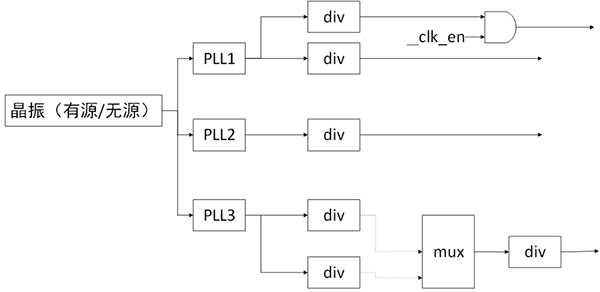
不同的clock设置,需要从某个或某几个时钟源头而来,最终开枝散叶,形成一颗时钟树。可通过 cat /sys/kernel/debug/clk/clk_summary 查看这棵时钟树。
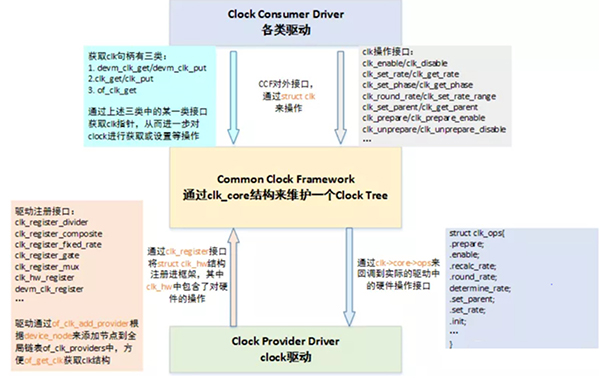
内核中用 CCF 框架来管理 clock,如下所示,右边是 clock 提供者,即 Clock Provider;中间是 CCF;左边是设备驱动的 clock 使用者,即 Clock Consumer。
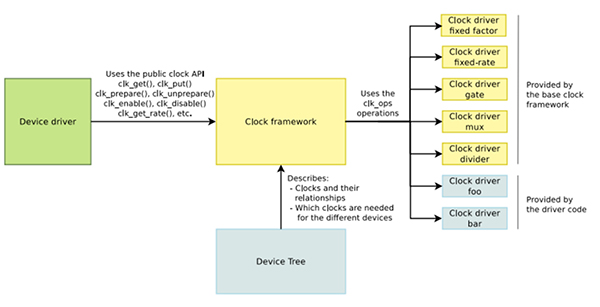
Clock Provider
- 根节点一般是 Oscillator(有源振荡器)或者 Crystal(无源振荡器)。
- 中间节点有很多种,包括 PLL(锁相环,用于提升频率的),Divider(分频器,用于降频的),Mux(从多个clock path中选择一个),Gate(用来控制ON/OFF的)。
- 叶节点是使用 clock 做为输入的、有具体功能的 HW block。
根据 clock 的特点,clock framework 将 clock 分为 fixed rate、gate、devider、mux、fixed factor、composite 六类。
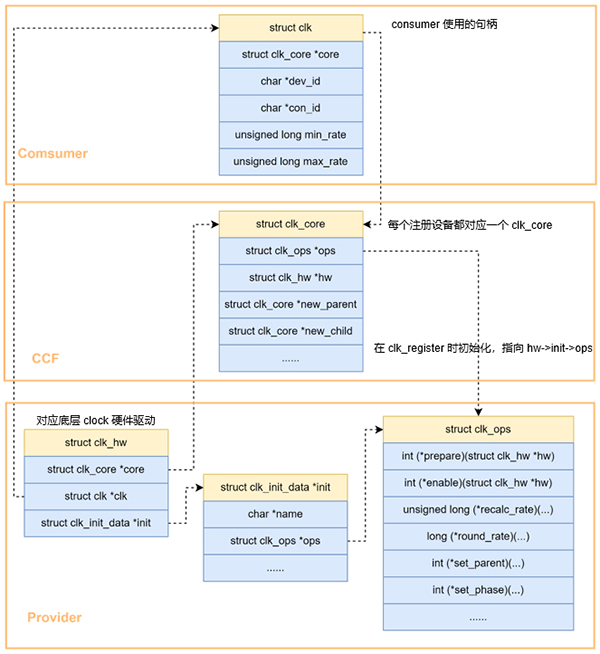
数据结构
上面六类本质上都属于clock device,内核把这些 clock HW block 的特性抽取出来,用 struct clk_hw 来表示,具体如下:
struct clk_hw {
//指向CCF模块中对应 clock device 实例
struct clk_core *core;
//clk是访问clk_core的实例。每当consumer通过clk_get对CCF中的clock device(也就是clk_core)发起访问的时候都需要获取一个句柄,也就是clk
struct clk *clk;
//clock provider driver初始化时的数据,数据被用来初始化clk_hw对应的clk_core数据结构。
const struct clk_init_data *init;
};
struct clk_init_data {
//该clock设备的名字
const char *name;
//clock provider driver进行具体的 HW 操作
const struct clk_ops *ops;
//描述该clk_hw的拓扑结构
const char * const *parent_names;
const struct clk_parent_data *parent_data;
const struct clk_hw **parent_hws;
u8 num_parents;
unsigned long flags;
};
以固定频率的振动器 fixed rate 为例,它的数据结构是:
struct clk_fixed_rate {
//下面是fixed rate这种clock device特有的成员
struct clk_hw hw;
//基类
unsigned long fixed_rate;
unsigned long fixed_accuracy;
u8 flags;
};
其他的特定的clock device大概都是如此,这里就不赘述了。
这里用一张图描述这些数据结构之间的关系:
注册方式
理解了数据结构,我们再看下每类 clock device 的注册方式。
1. fixed rate clock
这一类clock具有固定的频率,不能开关、不能调整频率、不能选择parent,是最简单的一类clock。可以直接通过 DTS 配置的方式支持。也可以通过接口,可以直接注册 fixed rate clock,如下:
CLK_OF_DECLARE(fixed_clk, "fixed-clock", of_fixed_clk_setup);
struct clk *clk_register_fixed_rate(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
unsigned long fixed_rate);
2. gate clock
这一类clock只可开关(会提供.enable/.disable回调),可使用下面接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_gate(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 bit_idx,
u8 clk_gate_flags, spinlock_t *lock);
3. divider clock
这一类clock可以设置分频值(因而会提供.recalc_rate/.set_rate/.round_rate回调),可通过下面两个接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_divider(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_divider_flags, spinlock_t *lock);
struct clk *clk_register_divider_table(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_divider_flags, const struct clk_div_table *table,
spinlock_t *lock);
4. mux clock
这一类clock可以选择多个parent,因为会实现.get_parent/.set_parent/.recalc_rate回调,可通过下面两个接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_mux(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char **parent_names, u8 num_parents, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_mux_flags, spinlock_t *lock);
struct clk *clk_register_mux_table(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char **parent_names, u8 num_parents, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u32 mask,
u8 clk_mux_flags, u32 *table, spinlock_t *lock);
5. fixed factor clock
这一类clock具有固定的factor(即multiplier和divider),clock的频率是由parent clock的频率,乘以mul,除以div,多用于一些具有固定分频系数的clock。由于parent clock的频率可以改变,因而fix factor clock也可该改变频率,因此也会提供.recalc_rate/.set_rate/.round_rate等回调。可通过下面接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_fixed_factor(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
unsigned int mult, unsigned int div);
6. composite clock
顾名思义,就是mux、divider、gate等clock的组合,可通过下面接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_composite(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char **parent_names, int num_parents,
struct clk_hw *mux_hw, const struct clk_ops *mux_ops,
struct clk_hw *rate_hw, const struct clk_ops *rate_ops,
struct clk_hw *gate_hw, const struct clk_ops *gate_ops,
unsigned long flags);
这些注册函数最终都会通过函数 clk_register 注册到 Common Clock Framework 中,返回为 struct clk 指针。如下所示:
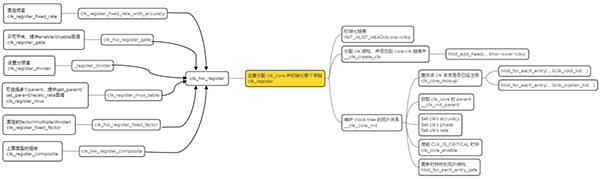
然后将返回的 struct clk 指针,保存在一个数组中,并调用 of_clk_add_provider 接口,告知 Common Clock Framework。
Clock Consumer
获取 clock
即通过 clock 名称获取 struct clk 指针的过程,由 clk_get、devm_clk_get、clk_get_sys、of_clk_get、of_clk_get_by_name、of_clk_get_from_provider 等接口负责实现,这里以 clk_get 为例,分析其实现过程:
struct clk *clk_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id)
{
const char *dev_id = dev ? dev_name(dev) : NULL;
struct clk *clk;
if (dev) {
//通过扫描所有“clock-names”中的值,和传入的name比较,如果相同,获得它的index(即“clock-names”中的第几个),调用of_clk_get,取得clock指针。
clk = __of_clk_get_by_name(dev->of_node, dev_id, con_id);
if (!IS_ERR(clk) || PTR_ERR(clk) == -EPROBE_DEFER)
return clk;
}
return clk_get_sys(dev_id, con_id);
}
struct clk *of_clk_get(struct device_node *np, int index)
{
struct of_phandle_args clkspec;
struct clk *clk;
int rc;
if (index < 0)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
rc = of_parse_phandle_with_args(np, "clocks", "#clock-cells", index,
&clkspec);
if (rc)
return ERR_PTR(rc);
//获取clock指针
clk = of_clk_get_from_provider(&clkspec);
of_node_put(clkspec.np);
return clk;
}
of_clk_get_from_provider 通过便利 of_clk_providers 链表,并调用每一个 provider 的 get 回调函数,获取 clock 指针。如下:
struct clk *of_clk_get_from_provider(struct of_phandle_args *clkspec)
{
struct of_clk_provider *provider;
struct clk *clk = ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
/* Check if we have such a provider in our array */
mutex_lock(&of_clk_lock);
list_for_each_entry(provider, &of_clk_providers, link) {
if (provider->node == clkspec->np)
clk = provider->get(clkspec, provider->data);
if (!IS_ERR(clk))
break;
}
mutex_unlock(&of_clk_lock);
return clk;
}
至此,Consumer 与 Provider 里讲的 of_clk_add_provider 对应起来了。
操作 clock
//启动clock前的准备工作/停止clock后的善后工作。可能会睡眠。
int clk_prepare(struct clk *clk)
void clk_unprepare(struct clk *clk)
//启动/停止clock。不会睡眠。
static inline int clk_enable(struct clk *clk)
static inline void clk_disable(struct clk *clk)
//clock频率的获取和设置
static inline unsigned long clk_get_rate(struct clk *clk)
static inline int clk_set_rate(struct clk *clk, unsigned long rate)
static inline long clk_round_rate(struct clk *clk, unsigned long rate)
//获取/选择clock的parent clock
static inline int clk_set_parent(struct clk *clk, struct clk *parent)
static inline struct clk *clk_get_parent(struct clk *clk)
//将clk_prepare和clk_enable组合起来,一起调用。将clk_disable和clk_unprepare组合起来,一起调用
static inline int clk_prepare_enable(struct clk *clk)
static inline void clk_disable_unprepare(struct clk *clk)
总结