platform总线是学习linux驱动必须要掌握的一个知识点。
本文参考已发布:Linux 3.14内核
一、概念
嵌入式系统中有很多的物理总线:I2c、SPI、USB、uart、PCIE、APB、AHB
linux从2.6起就加入了一套新的驱动管理和注册的机制platform平台总线,是一条虚拟的总线,并不是一个物理的总线。
相比 PCI、USB,它主要用于描述SOC上的片上资源。platform 所描述的资源有一个共同点:在CPU 的总线上直接取址。
平台设备会分到一个名称(用在驱动绑定中)以及一系列诸如地址和中断请求号(IRQ)之类的资源。
设备用platform_device表示,驱动用platform_driver进行注册。
与传统的bus/device/driver机制相比,platform由内核进行统一管理,在驱动中使用资源,提高了代码的安全性和可移植性。
二、platform
1. platform总线两个最重要的结构体
platform维护的所有的驱动都必须要用该结构体定义:
platform_driver
- struct platform_driver {
- int (*probe)(struct platform_device *); //
- int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
- void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
- int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
- int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
- struct device_driver driver;
- const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
- bool prevent_deferred_probe;
- };
该结构体,用于注册驱动到platform总线,
| 成员 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| probe | 当驱动和硬件信息匹配成功之后,就会调用probe函数,驱动所有的资源的注册和初始化全部放在probe函数中 |
| remove | 硬件信息被移除了,或者驱动被卸载了,全部要释放,释放资源的操作就放在该函数中 |
| struct device_driver driver | 内核维护的所有的驱动必须包含该成员,通常driver->name用于和设备进行匹配 |
| const struct platform_device_id *id_table | 往往一个驱动可能能同时支持多个硬件,这些硬件的名字都放在该结构体数组中 |
我们编写驱动的时候往往需要填充以上几个成员
platform_device
platform总线用于描述设备硬件信息的结构体,包括该硬件的所有资源(io,memory、中断、DMA等等)。
- struct platform_device {
- const char *name;
- int id;
- bool id_auto;
- struct device dev;
- u32 num_resources;
- struct resource *resource;
- const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
- /* MFD cell pointer */
- struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;
- /* arch specific additions */
- struct pdev_archdata archdata;
- };
| 成员 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| const char *name | 设备的名字,用于和驱动进行匹配的 |
| struct device dev | 内核中维护的所有的设备必须包含该成员, |
| u32 num_resources | 资源个数 |
| struct resource *resource | 描述资源 |
struct device dev->release()必须实现,
其中描述硬件信息的成员struct resource
0x139d0000
- struct resource {
- resource_size_t start; //表示资源的起始值,
- resource_size_t end; //表示资源的最后一个字节的地址, 如果是中断,end和satrt相同
- const char *name; // 可不写
- unsigned long flags; //资源的类型
- struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child;
- };
- flags的类型说明
- #define IORESOURCE_MEM 0x00000200 //内存
- #define IORESOURCE_IRQ 0x00000400 //中断
内核管理的所有的驱动,都必须包含一个叫struct device_driver成员, //男性描述的硬件,必须包含struct device结构体成员。 //女性
- struct device_driver {
- const char *name;
- struct bus_type *bus;
- struct module *owner;
- const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
- bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
- const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
- const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;
- int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
- int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
- void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);
- int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
- int (*resume) (struct device *dev);
- const struct attribute_group **groups;
- const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
- struct driver_private *p;
- };
其中:
- const char *name;
用于和硬件进行匹配。
内核描述硬件,必须包含struct device结构体成员:
- struct device {
- struct device *parent;
- struct device_private *p;
- struct kobject kobj;
- const char *init_name; /* initial name of the device */
- const struct device_type *type;
- struct mutex mutex; /* mutex to synchronize calls to
- * its driver.
- */
- struct bus_type *bus; /* type of bus device is on */
- struct device_driver *driver; /* which driver has allocated this
- device */
- void *platform_data; /* Platform specific data, device
- core doesn't touch it */
- struct dev_pm_info power;
- struct dev_pm_domain *pm_domain;
- #ifdef CONFIG_PINCTRL
- struct dev_pin_info *pins;
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
- int numa_node; /* NUMA node this device is close to */
- #endif
- u64 *dma_mask; /* dma mask (if dma'able device) */
- u64 coherent_dma_mask;/* Like dma_mask, but for
- alloc_coherent mappings as
- not all hardware supports
- 64 bit addresses for consistent
- allocations such descriptors. */
- struct device_dma_parameters *dma_parms;
- struct list_head dma_pools; /* dma pools (if dma'ble) */
- struct dma_coherent_mem *dma_mem; /* internal for coherent mem
- override */
- #ifdef CONFIG_DMA_CMA
- struct cma *cma_area; /* contiguous memory area for dma
- allocations */
- #endif
- /* arch specific additions */
- struct dev_archdata archdata;
- struct device_node *of_node; /* associated device tree node */
- struct acpi_dev_node acpi_node; /* associated ACPI device node */
- dev_t devt; /* dev_t, creates the sysfs "dev" */
- u32 id; /* device instance */
- spinlock_t devres_lock;
- struct list_head devres_head;
- struct klist_node knode_class;
- struct class *class;
- const struct attribute_group **groups; /* optional groups */
- void (*release)(struct device *dev);
- struct iommu_group *iommu_group;
- bool offline_disabled:1;
- bool offline:1;
- };
其中:
- void (*release)(struct device *dev);
不能为空。
2. 如何注册
要用注册一个platform驱动的步骤
1)注册驱动platform_device_register
- /**
- * platform_device_register - add a platform-level device
- * @pdev: platform device we're adding
- */
- int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *pdev)
- {
- device_initialize(&pdev->dev);
- arch_setup_pdev_archdata(pdev);
- return platform_device_add(pdev);
- }
2) 注册设备platform_driver_register
- #define platform_driver_register(drv) \
- __platform_driver_register(drv, THIS_MODULE)
三、举例
1. 开发步骤
platform 总线下驱动的开发步骤是:
设备
需要实现的结构体是:platform_device 。
1)初始化 resource 结构变量
2)初始化 platform_device 结构变量
3)向系统注册设备:platform_device_register。
以上三步,必须在设备驱动加载前完成,即执行platform_driver_register()之前,原因是驱动注册时需要匹配内核中所有已注册的设备名。
platform_driver_register()中添加device到内核最终还是调用的device_add函数。
Platform_device_add和device_add最主要的区别是多了一步insert_resource(p, r),即将platform资源(resource)添加进内核,由内核统一管理。
驱动
驱动注册中,需要实现的结构体是:platform_driver 。
在驱动程序的初始化函数中,调用了platform_driver_register()注册 platform_driver 。
需要注意的是:platform_driver 和 platform_device 中的 name 变量的值必须是相同的【在不考虑设备树情况下,关于设备树,后面会写新的文章详细讲述】 。
这样在 platform_driver_register() 注册时,会将当前注册的 platform_driver 中的 name 变量的值和已注册的所有 platform_device 中的 name 变量的值进行比较,只有找到具有相同名称的 platform_device 才能注册成功。
当注册成功时,会调用 platform_driver 结构元素 probe 函数指针。
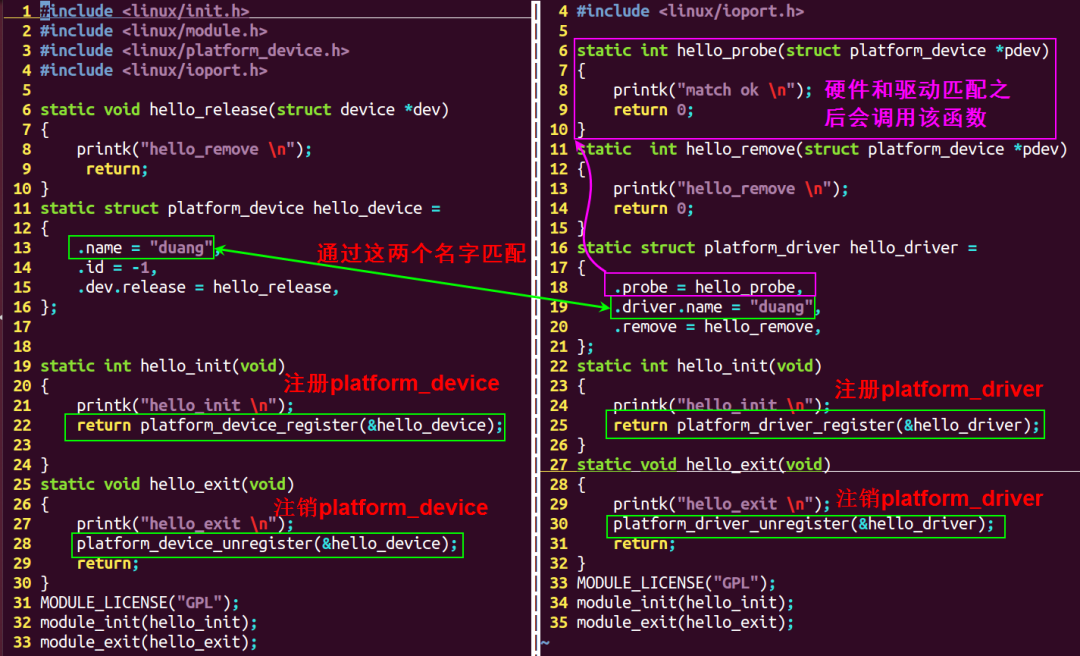
实例1
本例比较简单,只用于测试platform_driver 和platform_device是否可以匹配成功。
左边是platform_device结构体注册的代码,右边是platform_driver结构体注册的代码。
platform_driver 定义和注册:
- 1 #include <linux/init.h>
- 2 #include <linux/module.h>
- 3 #include <linux/platform_device.h>
- 4 #include <linux/ioport.h>
- 5
- 6 static int hello_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
- 7 {
- 8 printk("match ok \n");
- 9 return 0;
- 10 }
- 11 static int hello_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
- 12 {
- 13 printk("hello_remove \n");
- 14 return 0;
- 15 }
- 16 static struct platform_driver hello_driver =
- 17 {
- 18 .probe = hello_probe,
- 19 .driver.name = "duang",
- 20 .remove = hello_remove,
- 21 };
- 22 static int hello_init(void)
- 23 {
- 24 printk("hello_init \n");
- 25 return platform_driver_register(&hello_driver);
- 26 }
- 27 static void hello_exit(void)
- 28 {
- 29 printk("hello_exit \n");
- 30 platform_driver_unregister(&hello_driver);
- 31 return;
- 32 }
- 33 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- 34 module_init(hello_init);
- 35 module_exit(hello_exit);
platform_device定义和注册:
- 1 #include <linux/init.h>
- 2 #include <linux/module.h>
- 3 #include <linux/platform_device.h>
- 4 #include <linux/ioport.h>
- 5
- 6 static void hello_release(struct device *dev)
- 7 {
- 8 return;
- 9 }
- 10 static struct platform_device hello_device =
- 11 {
- 12 .name = "duang",
- 13 .id = -1,
- 14 .dev.release = hello_release,
- 15 };
- 16
- 17
- 18 static int hello_init(void)
- 19 {
- 20 printk("hello_init \n");
- 21 return platform_device_register(&hello_device);
- 22
- 23 }
- 24 static void hello_exit(void)
- 25 {
- 26 printk("hello_exit \n");
- 27 platform_device_unregister(&hello_device);
- 28 return;
- 29 }
- 30 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- 31 module_init(hello_init);
- 32 module_exit(hello_exit);
该程序只用于测试platform框架是否可以成功匹配,struct platform_device hello_device 并没有设置任何硬件信息。
Makfile
- 1 ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
- 2 obj-m:=device.o driver.o
- 3 else
- 4 KDIR :=/lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
- 5 PWD :=$(shell pwd)
- 6 all:
- 7 make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
- 8 clean:
- 9 rm -f *.ko *.o *.mod.o *.symvers *.cmd *.mod.c *.order
- 0 endif
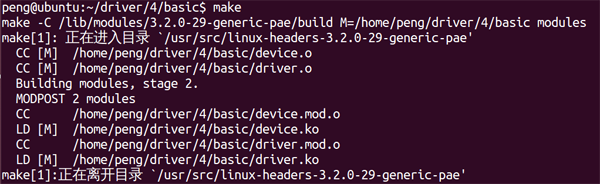
该makefile可以同时将两个C文件编译成ko文件。
编译:
编译
编译生成的文件:
在这里插入图片描述
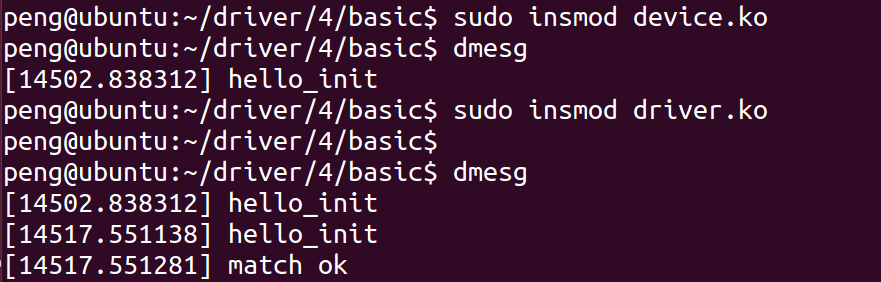
加载模块
- 清空log信息
- sudo dmesg -c
匹配成功
实例2
给结构体platform_device 增加硬件信息,并在内核中能够读取出来。本例向结构体hello_device 增加信息如下:
基址寄存器地址0x139d0000,该地址的空间是0x4
中断号199 【注意】 实际的内核中会把外设的中断号根据HW id(通常soc厂商设备soc的时候会给每一个中断源定义好唯一的ID)计算出一个新的中断号,该中断号会被cpu所识别。
device.c
- struct resource res[]={
- [0] ={
- .start = 0x139d0000,
- .end = 0x139d0000 + 0x3,
- .flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
- },
- [1] ={
- .start = 199,
- .end = 199,
- .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
- },
- };
- static struct platform_device hello_device =
- {
- .name = "duang",
- .id = -1,
- .dev.release = hello_release,
- .num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(res),
- .resource = res,
- };
driver.c
- static int hello_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
- {
- printk("match ok \n");
- printk("mem = %x \n",pdev->resource[0].start);
- printk("irq = %d \n",pdev->resource[1].start);
- //注册中断、申请内存
- return 0;
- }
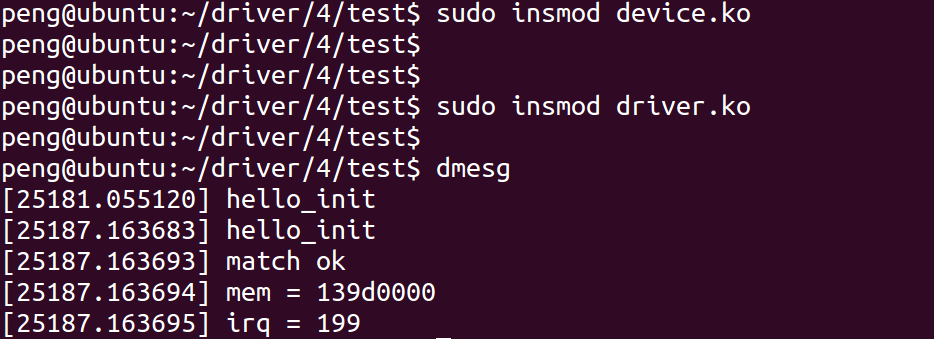
重新编译,卸载第一个例子的模块,并清除log:
- make
- sudo rmmod device
- sudo rmmod driver
- sudo dmesg -c
执行
由结果可知,probe函数正确读取到了硬件信息。
四、platform_device是如何管理的?
1. 没有设备树
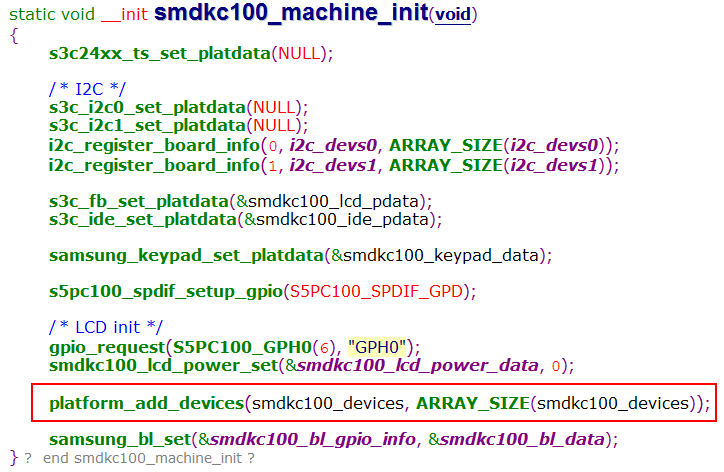
在没有设备树的时候,以三星Cortex-A8 s5pc100为例,硬件信息放在以下位置
- arch\arm\mach-s5pc100\Mach-smdkc100.c
- arch\arm\plat-samsung\
注册platform_device
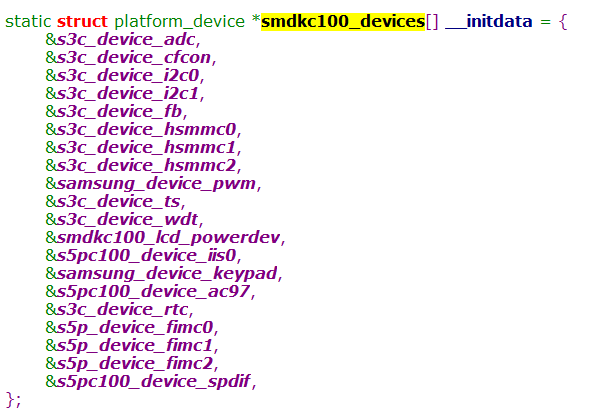
platform_device定义
该数组存放了,内核启动需要初始化的硬件的信息。
2. 如果有设备树
内核会有设备初始化的完整代码,会在内核启动的时候把设备树信息解析初始化,把硬件信息初始化到对应的链表中。在总线匹配成功后,会把硬件的信息传递给probe()函数。
四、总线相关的其他的知识点
1. 内核总线相关结构体变量
内核维护的所有的总线都需要用以下结构体注册一个变量。
- struct bus_type {
- const char *name;
- const char *dev_name;
- struct device *dev_root;
- struct device_attribute *dev_attrs; /* use dev_groups instead */
- const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;
- const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;
- const struct attribute_group **drv_groups;
- int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);
- int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
- int (*probe)(struct device *dev);
- int (*remove)(struct device *dev);
- void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);
- int (*online)(struct device *dev);
- int (*offline)(struct device *dev);
- int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
- int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
- const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
- struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;
- struct subsys_private *p;
- struct lock_class_key lock_key;
- };
platform总线变量的定义struct bus_type platform_bus_type定义如下:
- struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
- .name = "platform",
- .dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,
- .match = platform_match,
- .uevent = platform_uevent,
- .pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
- };
其中最重要的成员是**.match**。
当有设备的硬件信息注册到platform_bus_type 总线的时候,会遍历所有platform总线维护的驱动, 通过名字来匹配,如果相同,就说明硬件信息和驱动匹配,就会调用驱动的platform_driver ->probe函数,初始化驱动的所有资源,让该驱动生效。
当有设备的驱动注册到platform_bus_type 总线的时候,会遍历所有platform总线维护的硬件信息, 通过名字来匹配,如果相同,就说明硬件信息和驱动匹配,就会调用驱动的platform_driver ->probe函数,初始化驱动的所有资源,让该驱动生效。
注册位置
- drivers\base\Platform.c
platform_bus_type的注册
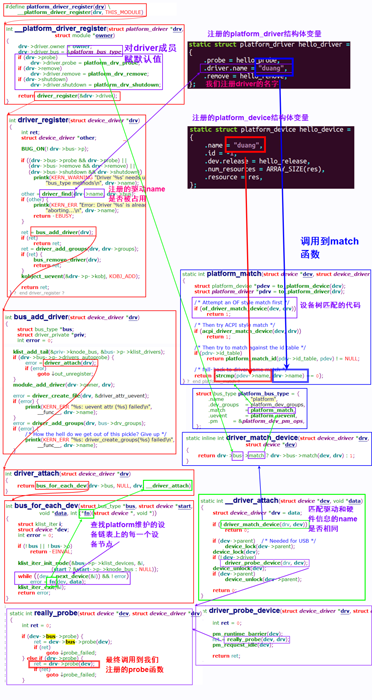
五、注册代码流程详解
捋架构的好处,就是可以帮助我们定位问题
1. match函数何时被调用到?
2. probe函数何时被调用到
以下是上述两个问题代码的调用流程:
代码调用流程
后面我们会再详细介绍设备树。
本文转载自微信公众号「一口Linux 」,可以通过以下二维码关注。转载本文请联系一口Linux 公众号。