许多管理员喜欢使用PowerShell来自动执行用户创建和文件夹权限管理这类组件功能,但是,虚拟化技术也可以通过命令行管理,包括微软Hyper-V。
推荐专题:Windows中的脚本技术-Windows Powershell
虽然有多种方法可以用PowerShell来管理Hyper-V,但本文将重点介绍如何免费使用Windows管理规范(WMI)脚本(来自CodePlex的开源工具)的方法。
在使用WMI脚本来管理Hyper-V之前,了解哪些类可用很重要。微软列出了大量的类。虽然相当完整,但他们不一定易于使用,并且总是不直观。因此,使用WMI来管理Hyper-V不适合心理承受能力弱的人。
使用PowerShell管理Hyper-V的比较流行方法之一是使用针对Hyper-V(PSHyperV)的PowerShell管理库。这是由James O’Neil所写的免费且开源的CodePlex项目。这是迄今为止***的选择。它提供一个完整cmdlet集给管理员使用,可以处理从虚拟机存储管理到网络管理的所有事情。让我们来了解其中的一些:
Get-VM——返回一个Hyper-V服务器上所有的虚拟机(见图1)。
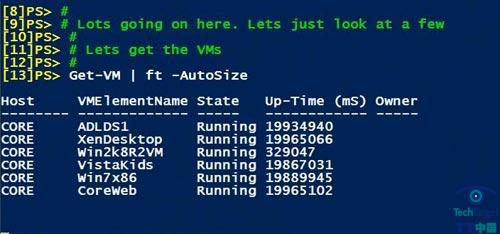
图1: Get-VM命令
下面的代码展示了Get-VM命令:
Function Get-VM
{# .ExternalHelp MAML-VM.XML
param(
[parameter(ValueFromPipeLine = $true)]
[ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()][Alias("VMName")]
$Name = "%",
[parameter()][ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
$Server = ".", #May need to look for VM(s) on Multiple servers
[Switch]$Suspended,
[switch]$Running,
[switch]$Stopped
)
Process {
# In case people are used to the * as a wildcard...
if ($Name.count -gt 1 ) {[Void]$PSBoundParameters.Remove("Name")
; $Name | ForEach-object {Get-VM -Name $_ @PSBoundParameters}}
if ($name -is [String]) {
$Name = $Name.Replace("*","%")
# Note in V1 the test was for caption like "Virtual%" which
did not work in languages other than English.
# Thanks to Ronald Beekelaar - we now test for a processID ,
the host has a null process ID, stopped VMs have an ID of 0.
$WQL = "SELECT * FROM MSVM_ComputerSystem WHERE ElementName
LIKE '$Name' AND ProcessID >= 0"
if ($Running -or $Stopped -or $Suspended) {
$state = ""
if ($Running) {$State += " or enabledState = " +
[int][VMState]::Running }
if ($Stopped) {$State += " or enabledState = " +
[int][VMState]::Stopped }
if ($Suspended) {$State += " or enabledState = " +
[int][VMState]::Suspended }
$state = $state.substring(4)
$WQL += " AND ($state)"
}
Get-WmiObject -computername $Server -NameSpace $HyperVNamespace -Query $WQL | Add-Member -MemberType ALIASPROPERTY -Name "VMElementName" -Value "ElementName" -PassThru
}
elseif ($name.__class) {
Switch ($name.__class) {
"Msvm_ComputerSystem" {$Name}
"Msvm_VirtualSystemSettingData" {get-wmiobject -
computername $Name.__SERVER -namespace $HyperVNamespace -Query
"associators of {$($name.__path)} where
resultclass=Msvm_ComputerSystem"}
Default get-wmiobject -
computername $Name.__SERVER -namespace $HyperVNamespace -Query
"associators of {$($Name.__path)} where
resultclass=Msvm_VirtualSystemSettingData" |
ForEach-Object
{$_.getRelated("Msvm_ComputerSystem")} | Select-object -unique }
}
}
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
如您所见,这段代码包含了WMI基本类和helper逻辑并报告了结果。
Get-VMSwitch——返回所有在Hyper-V服务器上的虚拟交换(见图2)。
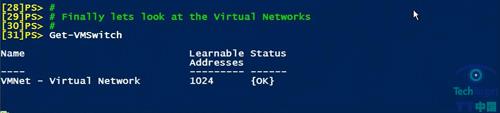
图2: Get-VMSwitch命令
下面的代码展示了Get-VMSwitch的命令:
Function Get-VMSwitch
{# .ExternalHelp MAML-VMNetwork.XML
param(
[parameter(ValueFromPipeline = $true)][Alias("Name")]
[String]$VirtualSwitchName="%",
[parameter()][ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
$Server = "." #Can query multiple servers for switches
)
process {
$VirtualSwitchName=$VirtualSwitchName.replace("*","%")
Get-WmiObject -computerName $server -NameSpace $HyperVNamespace
-query "Select * From MsVM_VirtualSwitch Where elementname like '$VirtualSwitchname' "
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
Get-VMSnapShot——提供所有在Hyper-V服务器上的快照(见图3)。
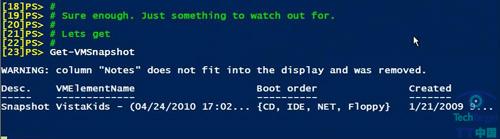
图3:Get-VMSnapShot命令
下面的语句展示了Get-VMSnapShot命令:
Function Get-VMSnapshot
{# .ExternalHelp MAML-VMSnapshot.XML
Param(
[parameter(Position=0 , ValueFromPipeline = $true)]
$VM = "%",
[String]$Name="%",
[parameter()][ValidateNotNullOrEmpty()]
$Server="." ,
[Switch]$Current,
[Switch]$Newest,
[Switch]$Root
)
process{
if ($VM -is [String]) {$VM=(Get-VM -Name $VM -Server $server) }
if ($VM.count -gt 1 ) {[Void]$PSBoundParameters.Remove("VM") ; $VM |
ForEach-object { Get-VMSnapshot -VM $_ @PSBoundParameters}}
if ($vm.__CLASS -eq 'Msvm_ComputerSystem') {
if ($current) {Get-wmiobject -computerNam $vm.__server -
Namespace $HyperVNamespace -q "associators of {$($vm.path)} where assocClass=MSvm_PreviousSettingData"}
else {$Snaps=Get-WmiObject -computerName $vm.__server -NameSpace $HyperVNameSpace -Query "Select * From MsVM_VirtualSystemSettingData Where systemName='$($VM.name)' and
instanceID <> 'Microsoft:$($VM.name)' and elementName like '$name' "
if ($newest) {$Snaps | sort-object -property
creationTime | select-object -last 1 }
elseif ($root) {$snaps | where-object {$_.parent -eq
$null} }
else {$snaps}
}
}
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
可以从CodePlex的网站上找到PSHyperV的多种附加功能来帮助管理员执行查找、操作和配置hypervisor的不同的组件等相关任务。
编写WMI包装器和使用PSHyperV,只是管理员用PowerShell来管理Hyper-V的一些方式。请注意,PSHyperV的***版本并不是完整的版本,因此,它不像其他软件那么稳定。
【编辑推荐】